
I am a specialist in Respiratory Medicine with special interest in Interventional Pulmonary, Allergy-Asthma, Immunology, Tuberculosis, Pleural diseases, Covid and post covid syndromes, Sleep Medicine, critical care and other Respiratory diseases.
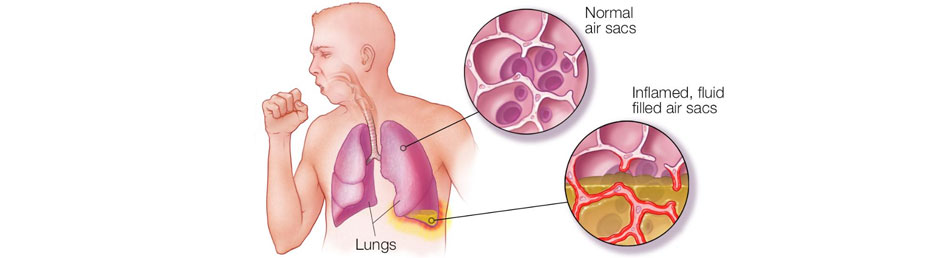
Pneumonia is an infection in one or both of your lungs caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. When there is an infection in the lungs, several things happen
Your lungs’ main job is to get oxygen into your blood and remove carbon dioxide. This happens during breathing. You breathe 12 to 20 times per minute when you are not sick. When you breathe in, air travels down the back of your throat and passes through your voice box and into your windpipe (trachea). Your trachea splits into two air passages (bronchial tubes). One bronchial tube leads to the left lung, the other to the right lung. For the lungs to perform their best, the airways need to be open as you breathe in and out. Swelling (inflammation) and mucus can make it harder to move air through the airways, making it harder to breathe. This leads to shortness of breath, difficulty breathing and feeling more tired than normal.
Pneumonia is spread when droplets of fluid containing the pneumonia bacteria or virus are launched in the air when someone coughs or sneezes and then inhaled by others. You can also get pneumonia from touching an object previously touched by the person with pneumonia (transferring the germs) or touching a tissue used by the infected person and then touching your mouth or nose.
Pneumonia can be caused by a wide variety of bacteria, viruses or fungi. Pneumonia is most commonly classified by the type of germ that causes it and by the location where the person became infected.
Community-acquired pneumonia is the most common type of pneumonia. This type of pneumonia occurs outside of a hospital or other healthcare facility.
