
I am a specialist in Respiratory Medicine with special interest in Interventional Pulmonary, Allergy-Asthma, Immunology, Tuberculosis, Pleural diseases, Covid and post covid syndromes, Sleep Medicine, critical care and other Respiratory diseases.
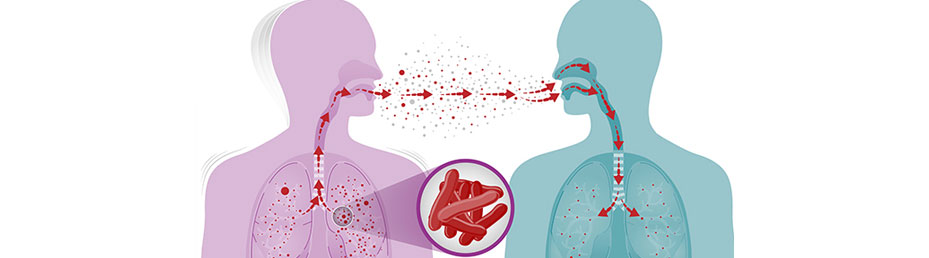
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs. The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from person to person through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes.
Once rare in developed countries, tuberculosis infections began increasing in 1985, partly because of the emergence of HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. HIV weakens a person's immune system, so it can't fight the TB germs. In the United States, because of stronger control programs, tuberculosis began to decrease again in 1993. But it remains a concern.
Many tuberculosis strains resist the drugs most used to treat the disease. People with active tuberculosis must take many types of medications for months to get rid of the infection and prevent antibiotic resistance.
Although your body can harbor the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, your immune system usually can prevent you from becoming sick. For this reason, doctors make a distinction between:
Signs and symptoms of active TB include:
Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria that spread from person to person through microscopic droplets released into the air. This can happen when someone with the untreated, active form of tuberculosis coughs, speaks, sneezes, spits, laughs or sings.
Although tuberculosis is contagious, it's not easy to catch. You're much more likely to get tuberculosis from someone you live or work with than from a stranger. Most people with active TB who've had appropriate drug treatment for at least two weeks are no longer contagious.
